[ad_1]
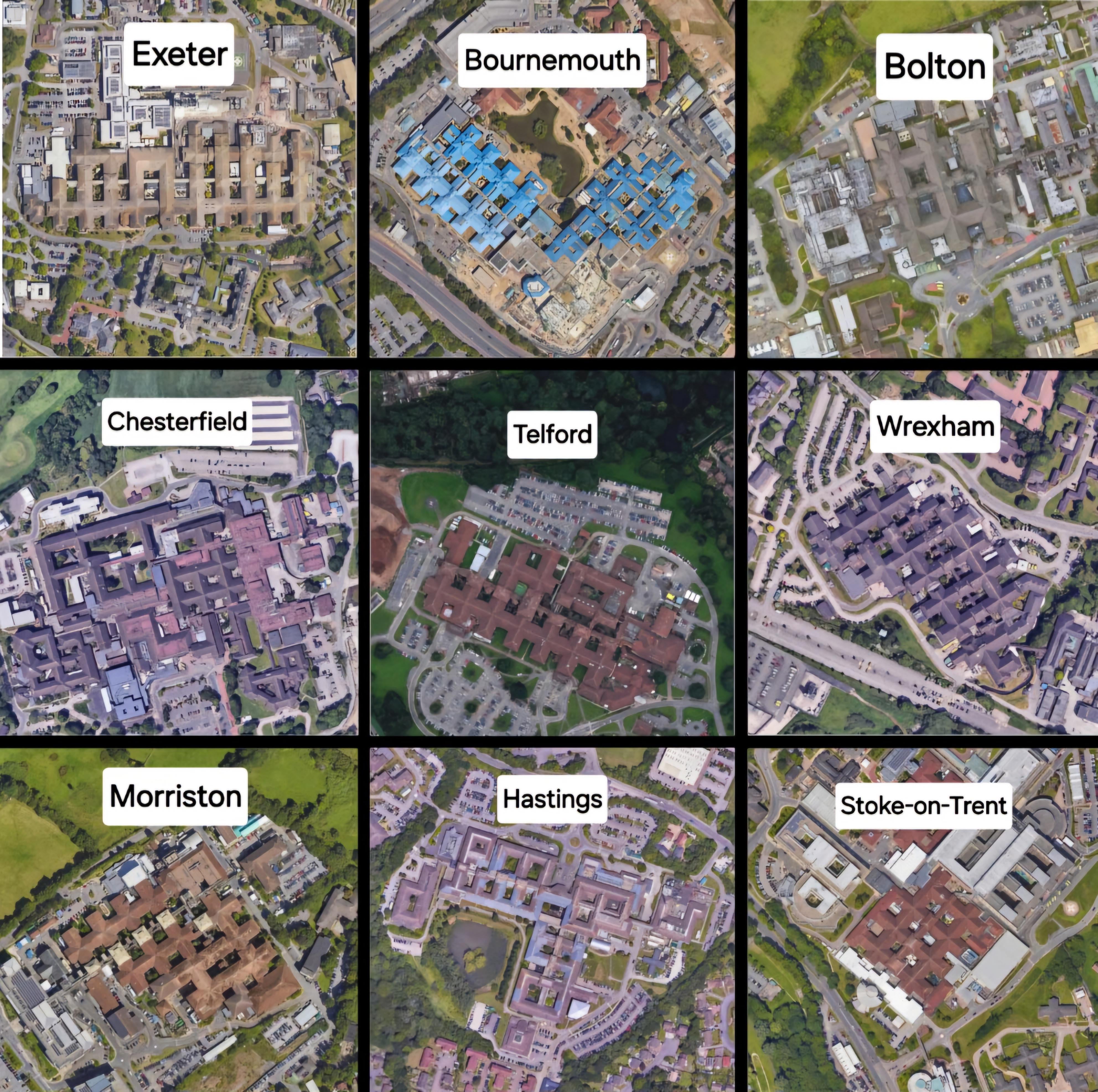
Many British hospital buildings are designed in a grid or waffle arrangement with multiple inner courtyards as a result of historical and practical factors.
One reason for this design is the influence of the Florence Nightingale, a pioneer in modern nursing and hospital design. Nightingale promoted the idea of having separate pavilions connected by open spaces to allow for better ventilation and natural light, which led to the grid-like layout seen in many hospitals in Britain.
Additionally, the grid layout allows for efficient organization and easy navigation within the hospital, ensuring that patients, staff, and visitors can easily find their way around the complex. The inner courtyards provide spaces for patients to relax and for staff to take breaks, promoting a healing environment within the hospital.
Moreover, the grid layout allows for expansion and adaptation of the hospital over time, as new buildings or wings can be added in a logical and organized manner. This flexibility is crucial for modern hospitals that may need to accommodate changing needs and technologies.
Overall, the grid/waffle arrangement with multiple inner courtyards in British hospital buildings is a result of a combination of historical influences, practical considerations, and a focus on creating healing environments that benefit patients, staff, and visitors alike.
